Optimizing, publishing and styling GeoTIFF data¶
Styling with CSS¶
The CSS extension module allows to build map styles using a compact, expressive styling language already well known to most web developers: Cascading Style Sheets.
The extension is available on GeoServer only. The standard CSS language has been extended to allow for map filtering and managing all the details of a map production. In this section we’ll experience creating a few simple styles with the CSS language.
Styling raster data¶
Go to the
srtm_boulderlayer details page and click onEditing Tools > Style > Edit
Add a new
Style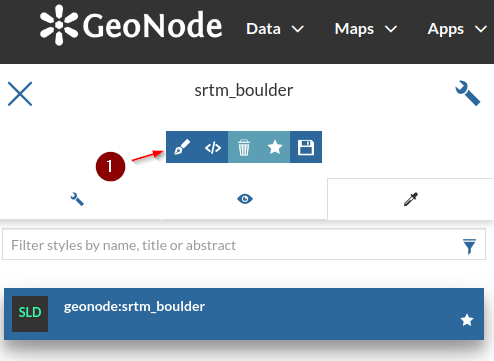
Select
CSSand click on the+button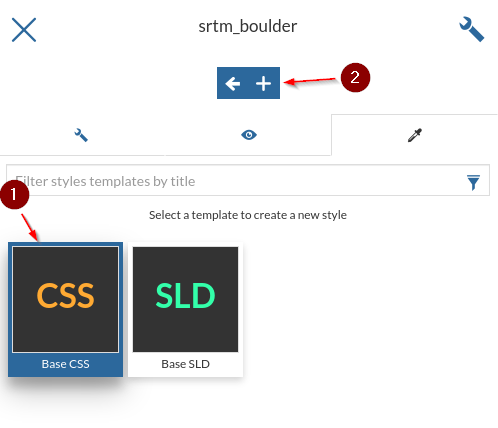
Put a name like
CSS Rasterand click onSave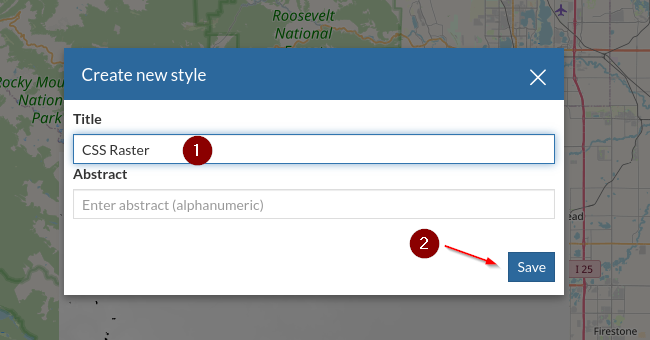
Modify the style you just created
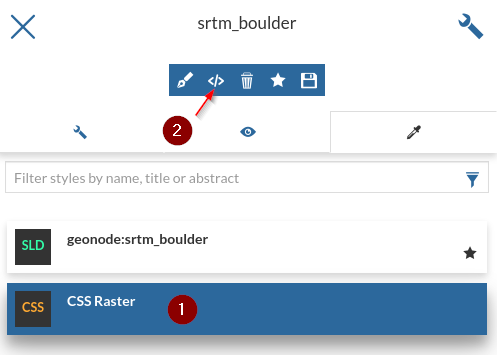
From the panel, switch to the advanced editor
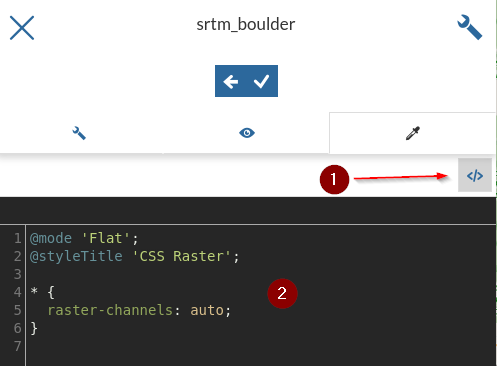
Insert the following
CSS, notice the changes directly on the map, andSave* { raster-channels: auto; raster-color-map: color-map-entry(black, 0, 0) color-map-entry(green, 1500) color-map-entry(yellow, 2000) color-map-entry(maroon, 3000) color-map-entry(white, 4000); }
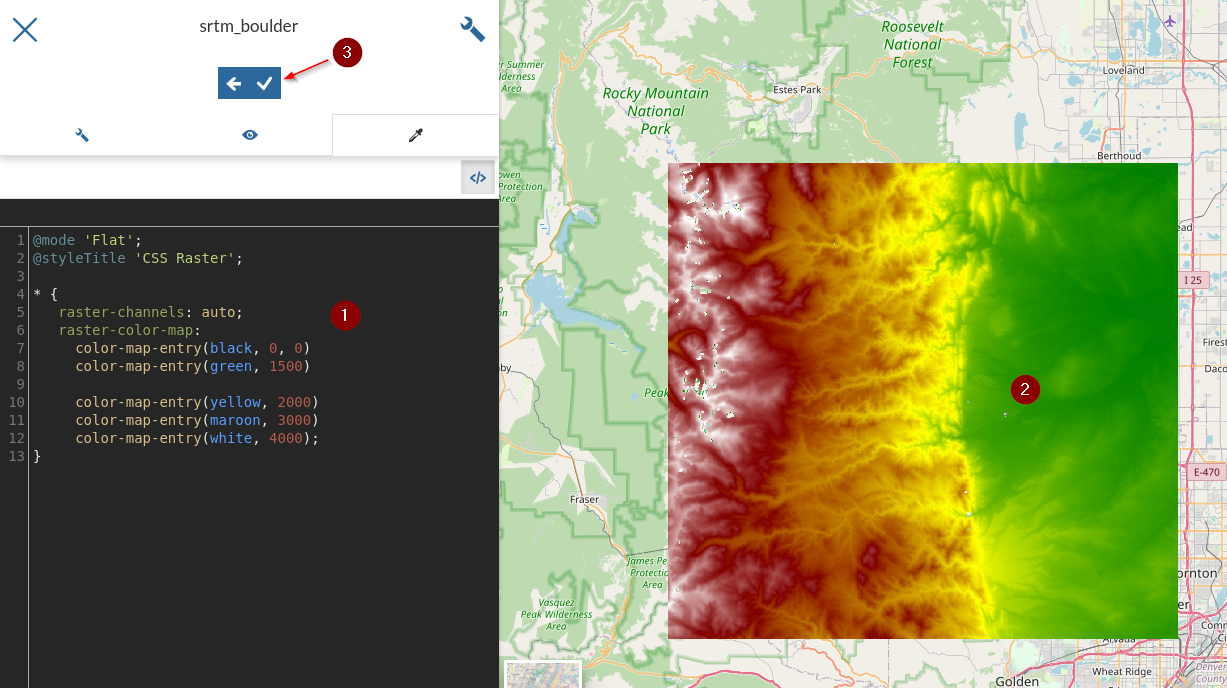
The
*at the beginning means that we will apply the rules at any zoom level; let’s add a rule to show the raster only above a certainscale denominator[@scale > 75000] { raster-channels: auto; raster-color-map: color-map-entry(black, 0, 0) color-map-entry(green, 1500) color-map-entry(yellow, 2000) color-map-entry(maroon, 3000) color-map-entry(white, 4000); }
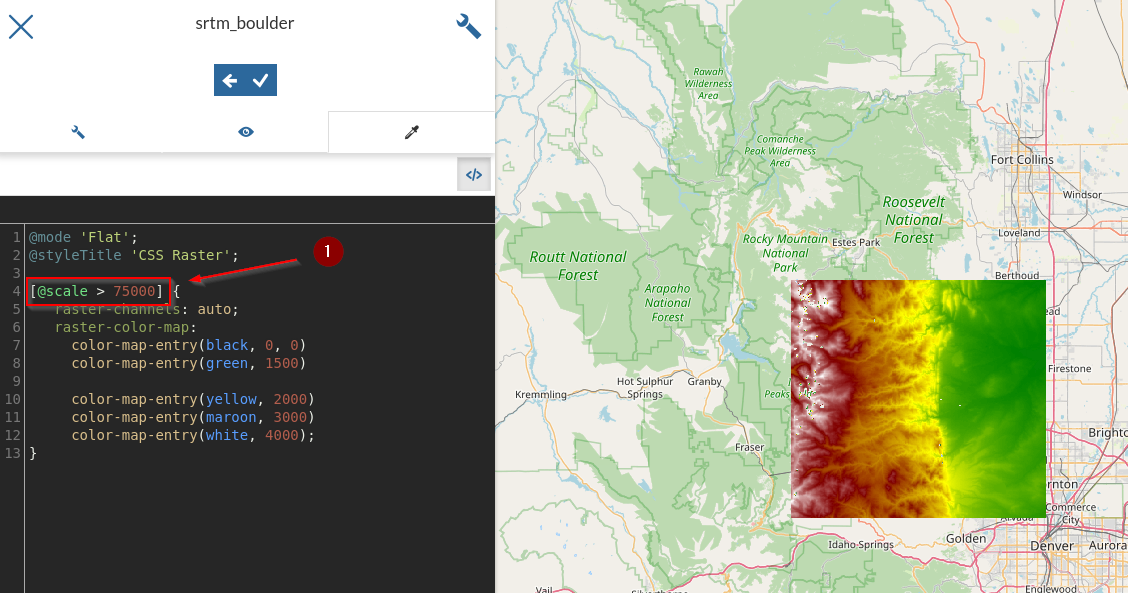
Try to zoom in and out by checking the
scale denominator; notice the raster appearing and disappearing accordingly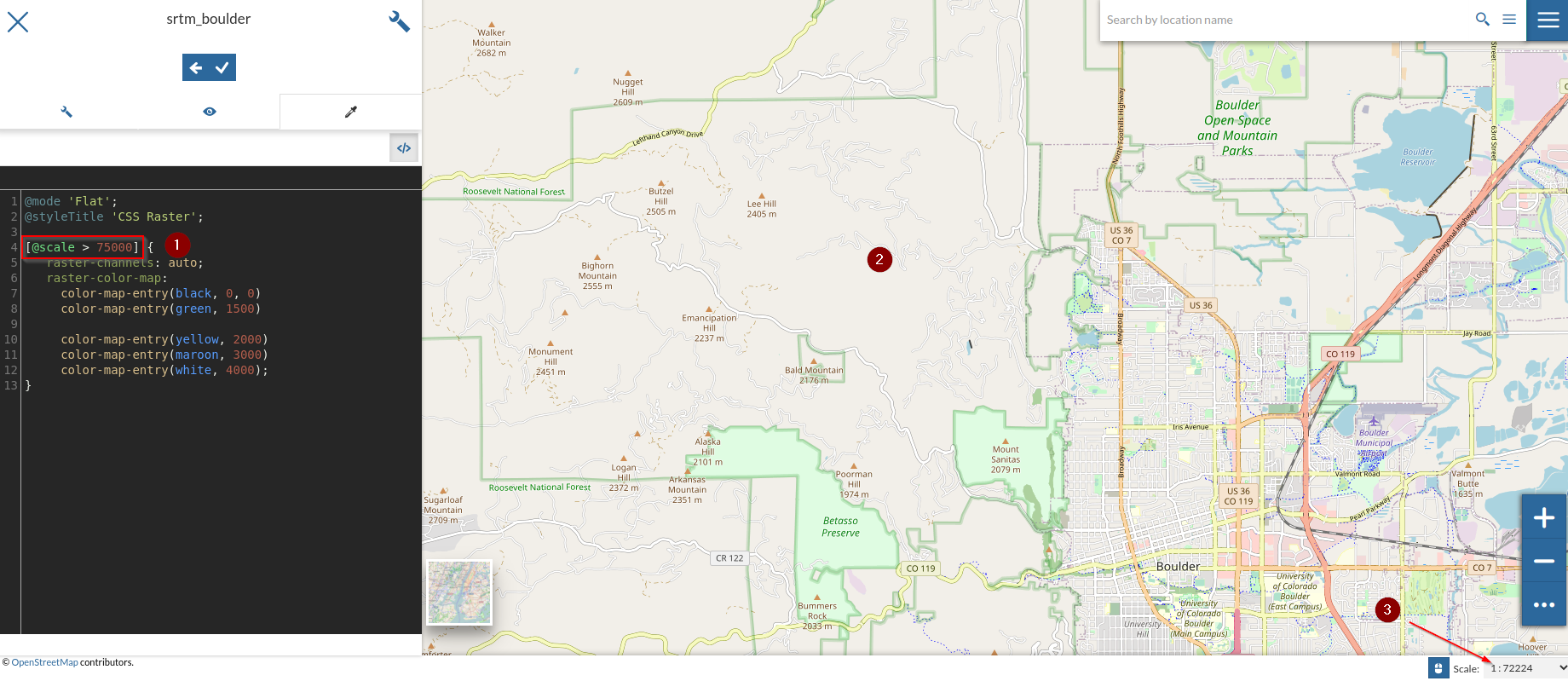
Nice Map with Hillshading¶
In this section we are going to create a hillshade raster computed from the srtm DEM of Boulder. We will use the GDAL utilities to do that, and in particular the gdaldem one, which has several options available.
Once we created the hillshade, we will add it to GeoNode, provide a nice style and then merge all together on a nice map.
Go to the
terminaland move to the folder/opt/data/sample_data/pretty_maps/data/boulder/Run the
gdaldemutility with the following optionsgdaldem hillshade -z 5 -s 111120 srtm_boulder.tiff srtm_boulder_hs.tiff -co tiled=yes
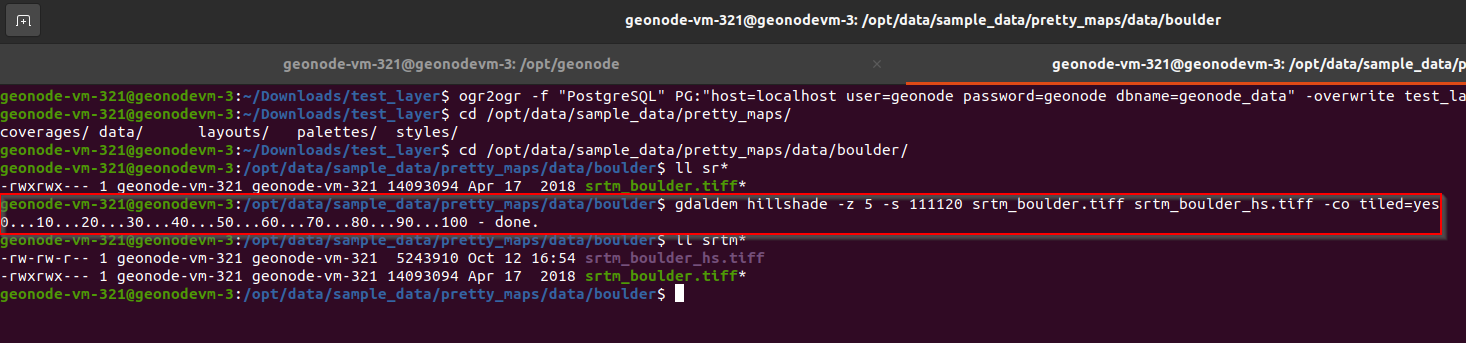
The z parameter exaggerates the elevation, the s parameter provides the ratio between the elevation units and the ground units (degrees in this case), -co tiled=yes makes gdaldem generate a TIFF with inner tiling. We’ll investigate this last option better in the following pages.
That will create a new
GeoTIFFcalledsrtm_boulder_hs.tiffUpload the new layer as user
test_user1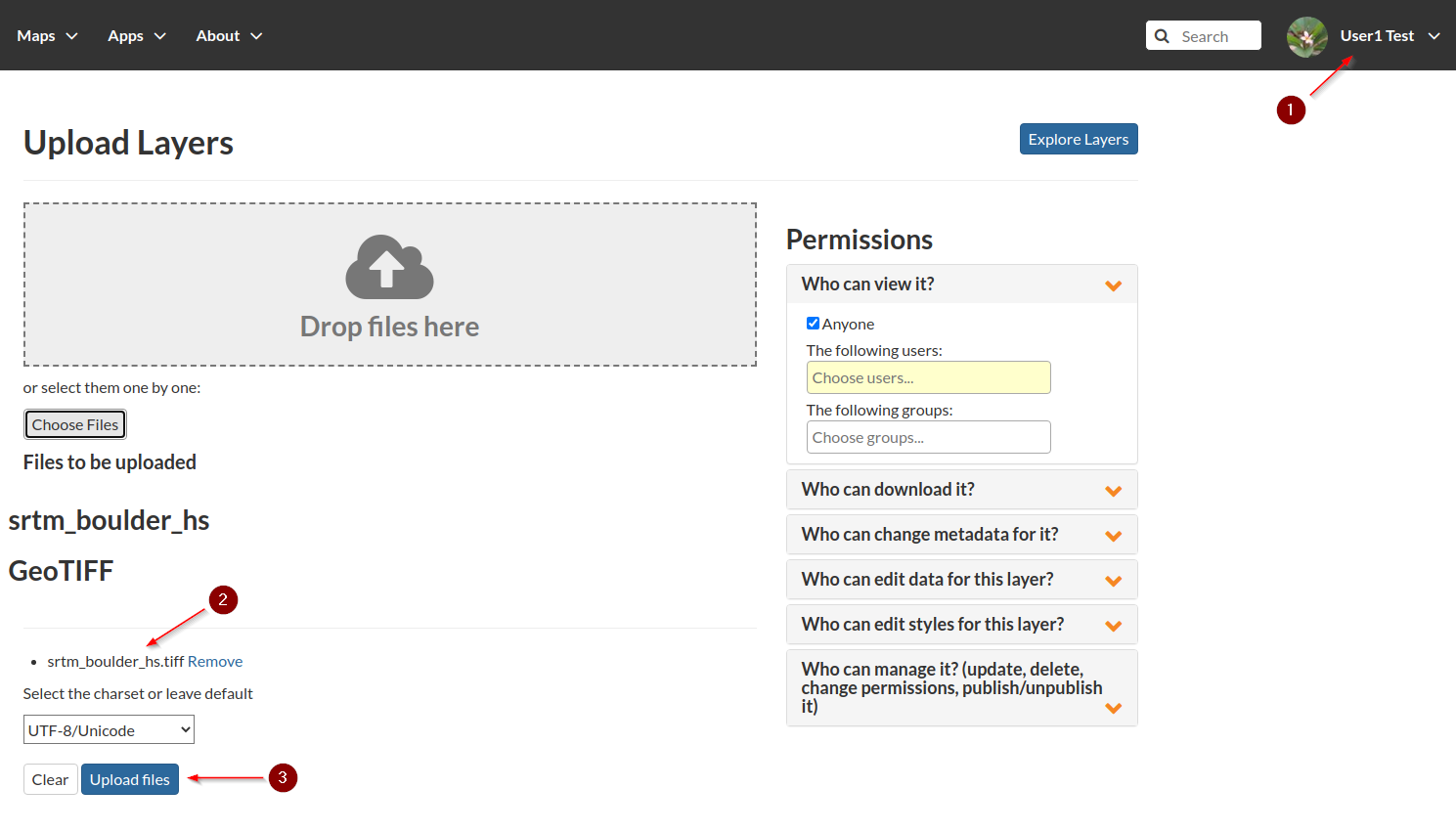
Edit the style for this layer too; a new
CSSnamedHillshade CSS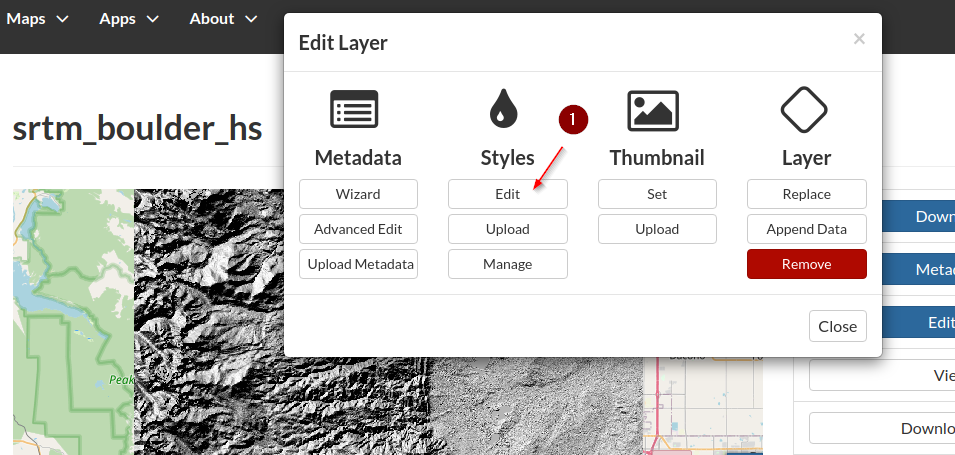
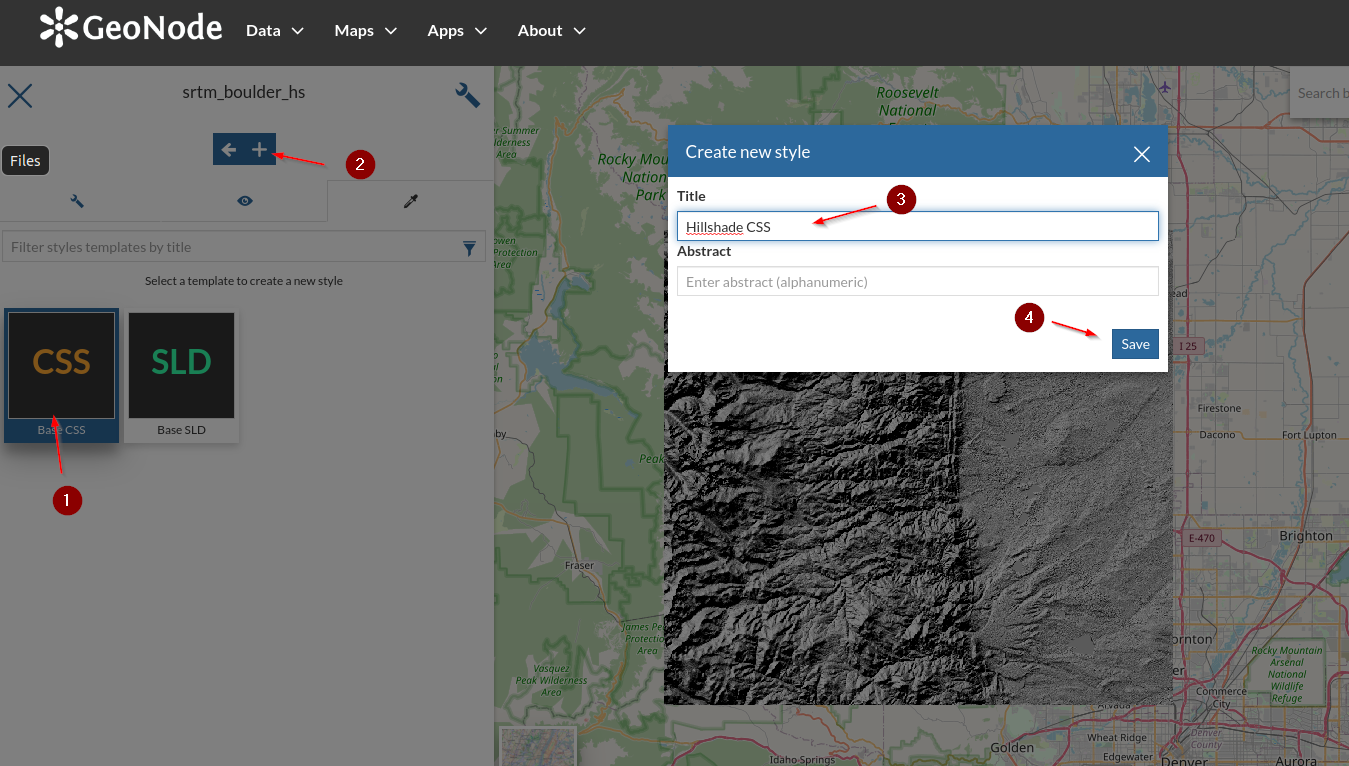
Insert the
CSSbelow and save[@scale > 75000] { raster-channels: auto; raster-color-map: color-map-entry(#000000, 0, 0) color-map-entry(#999999, 1) color-map-entry(#FFFFFF, 256); composite: 'multiply'; }
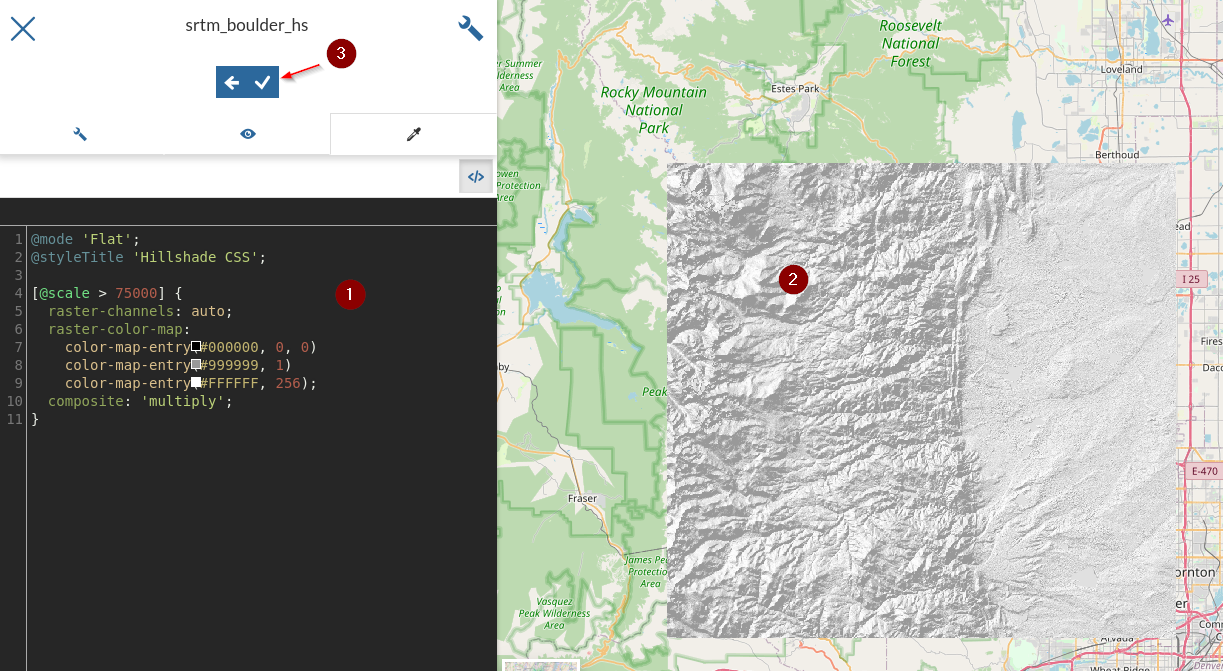
Note the “composite” vendor option, used to have the hillshading use a special color blending mode to get a better visual result compared to simple translucency
Create a new
Mapand add the two raster layers just updated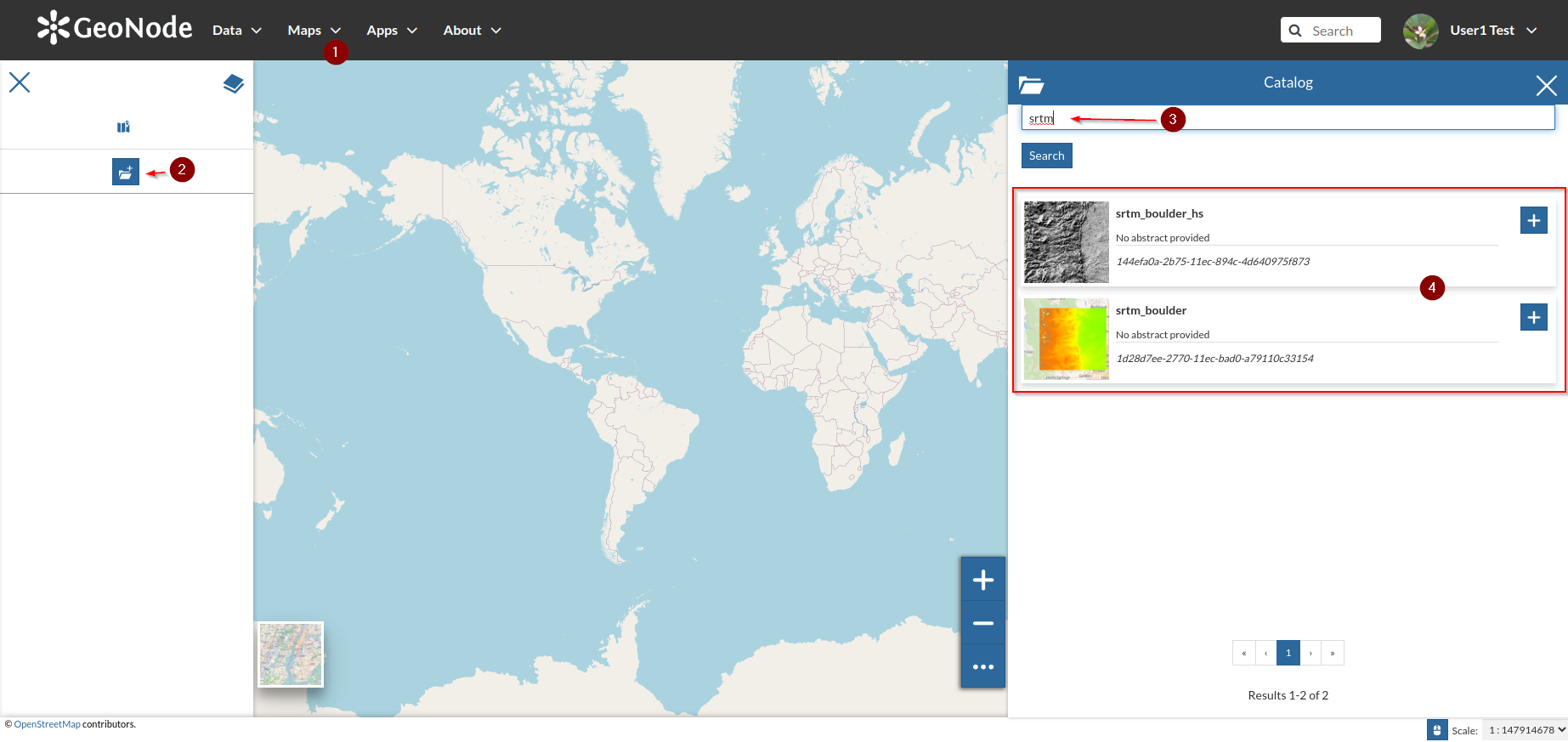
Highlight the
srtm_boulderand themodifyoption
Select the
styletab, click on theCSS Rasterstyle andSave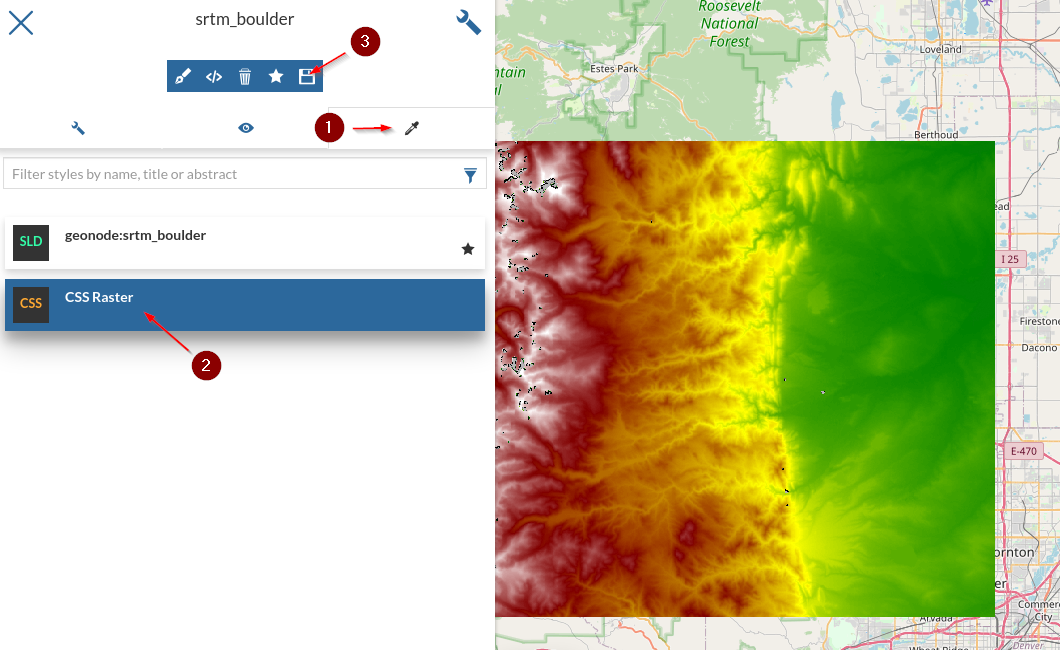
Notice the
legendhas changed and so the rendering on the map for that layer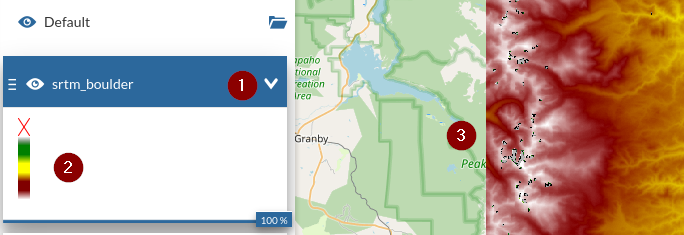
Similarly go ahead and select the
Hillshade CSSfor thesrtm_boulder_hslayer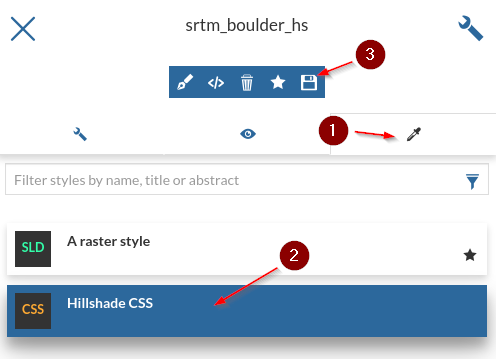
Adjust the overlays
orderandopacityand notice the map changing accordingly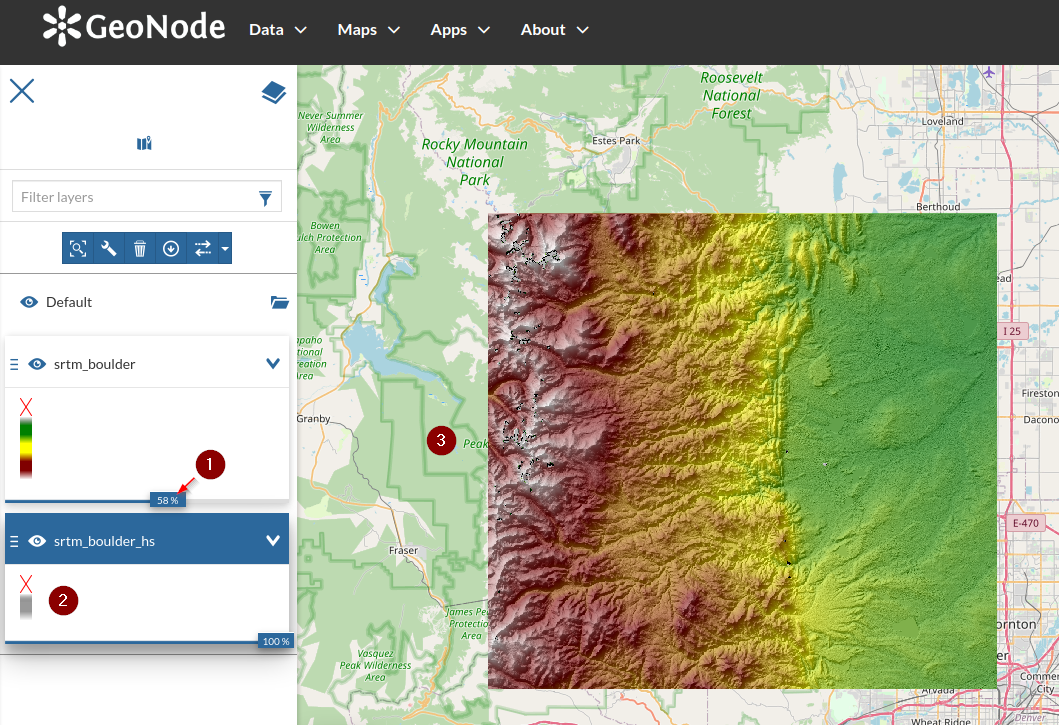
Zoom-in in order to highlight the details and the color effect enhanced by the hillshade
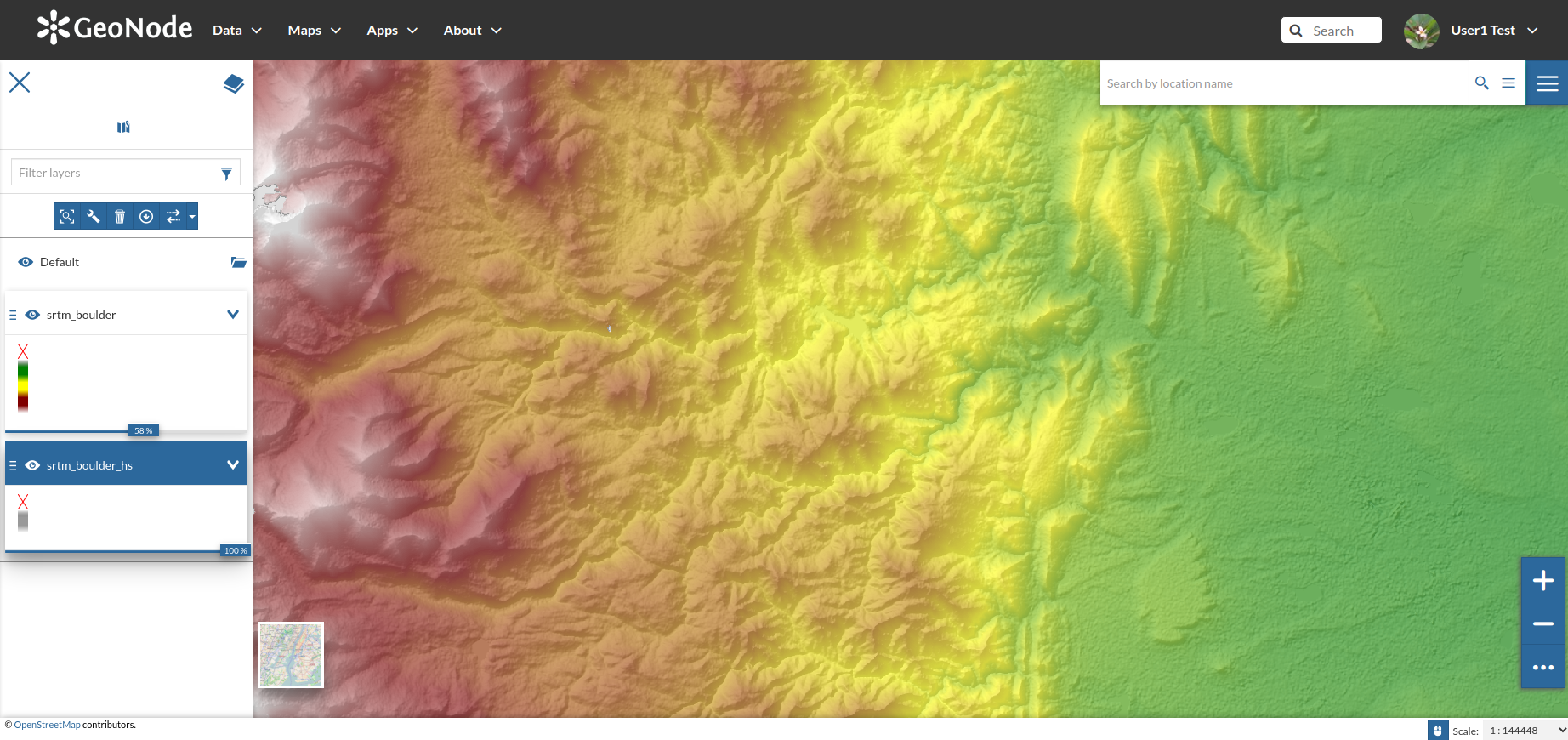
Save the new map when done
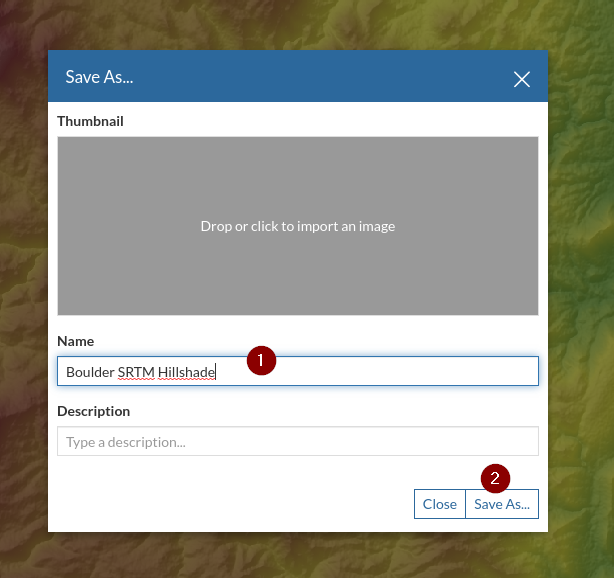
Adding and Optimizing Raster Image Mosaics¶
An Image Mosaic is composed of a set of layers which are exposed as a single coverage. The ImageMosaic format allows to automatically build and setup a mosaic from a set of georeferenced layers. This section provides better instructions to configure an Image Mosaic.
Publishing an Image Mosaic¶
In this section we are going to publish on GeoNode a mosaic of aerial orthophotos through the GeoServer ImageMosaic store.
We will need to do some preparation first.
Open a
terminaland move to the folder/opt/data/sample_data/user_data; change thewritepermissions of the folder namedaerialin order to allow the user to modify itcd /opt/data/sample_data/user_data sudo chmod -Rf 777 aerial
Move to
aerialand delete the filesaerial.propertiesandsample_image.datcd aerial rm aerial.properties sample_image.datCreate or edit a file named
indexer.propertieswith the following contentsvim indexer.properties
Caching=false Schema=*the_geom:Polygon,location:String
Create or edit a file named
datastore.propertieswith the following contentsvim datastore.properties
SPI=org.geotools.data.postgis.PostgisNGDataStoreFactory host=localhost port=5432 database=geonode_data schema=public user=geonode passwd=geonode Loose\ bbox=true Estimated\ extends=false validate\ connections=true Connection\ timeout=10 preparedStatements=true create\ database\ params=WITH\ TEMPLATE\=postgis20
Go to the GeoServer admin dahsboard; log in as an
adminand click onData > Stores > Add new store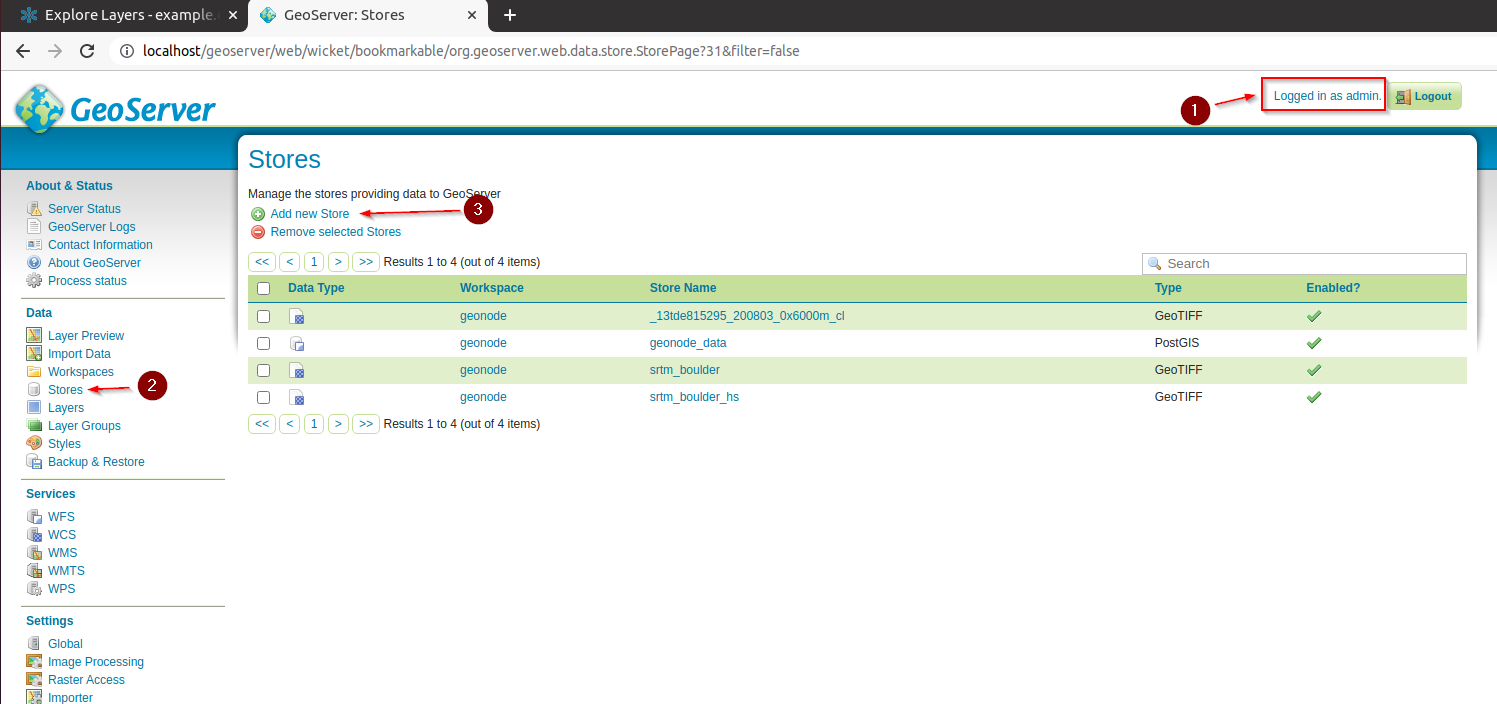
Select
ImageMosaicform the list of the availableRaster Data Sources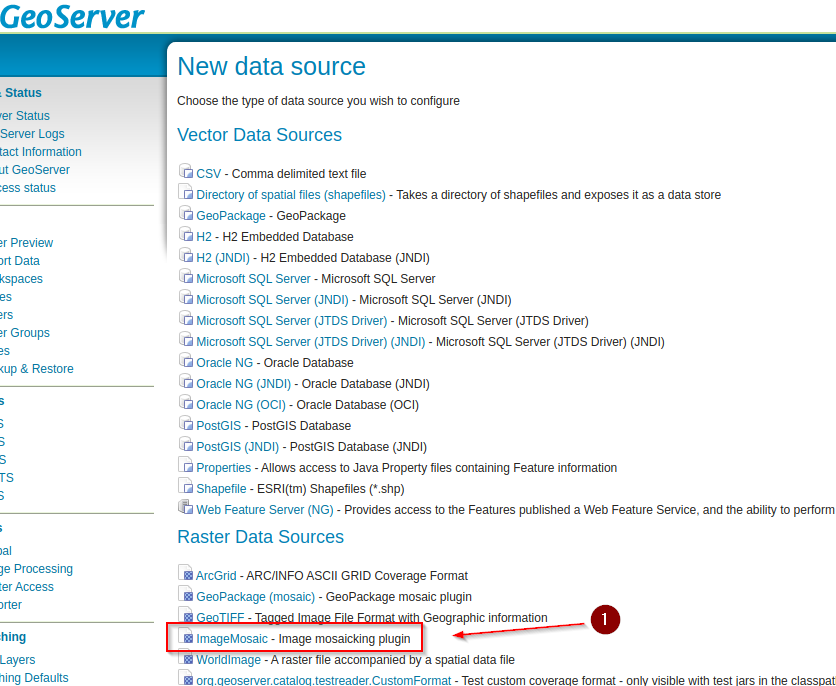
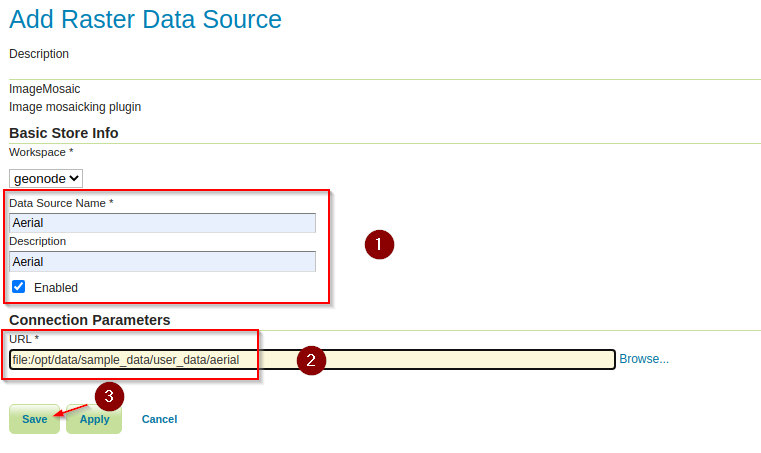
Provide the following inputs on the
ImageMosaicformName:
AerialTitle:
AerialURL*:
file:/opt/data/sample_data/user_data/aerial
On the next windows, click on
PublishandSavethe layer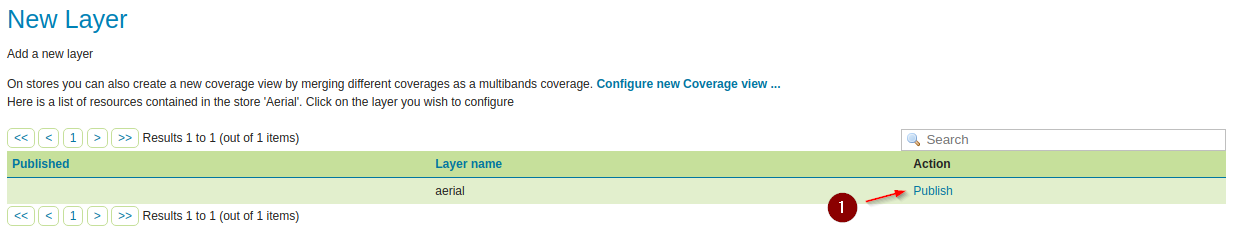
Move to the GeoServer
Layer Previewsection and open theOpenLayerspreview for theAeriellayer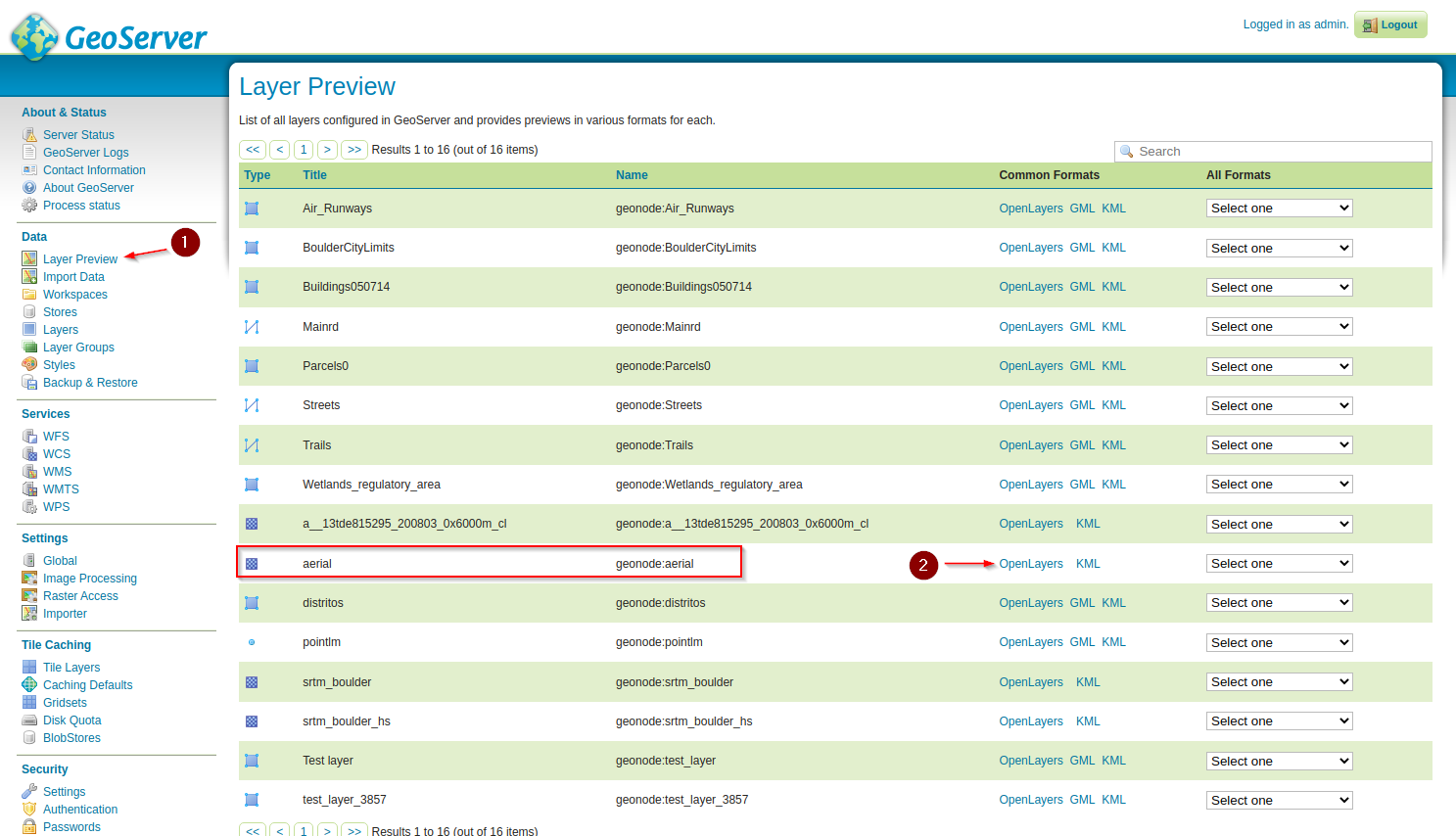
We will suddenly notice two issues mainly:
The load, pan and zoom is slow
There are some black tiles filling the bounding box

Optimizing an Image Mosaic¶
Open a
terminaland move to the folder/opt/data/sample_data/user_data; change thewritepermissions of the folder namedoptimizedin order to allow the user to modify itcd /opt/data/sample_data/user_data sudo chmod -Rf 777 optimized
Move to
optimizedand delete the filesoptimized.propertiesandsample_image.datcd optimized rm optimized.properties sample_image.datCreate or edit a file named
indexer.propertieswith the following contentsvim indexer.properties
Caching=false Schema=*the_geom:Polygon,location:String
Create or edit a file named
datastore.propertieswith the following contentsvim datastore.properties
SPI=org.geotools.data.postgis.PostgisNGDataStoreFactory host=localhost port=5432 database=geonode_data schema=public user=geonode passwd=geonode Loose\ bbox=true Estimated\ extends=false validate\ connections=true Connection\ timeout=10 preparedStatements=true create\ database\ params=WITH\ TEMPLATE\=postgis20
Add a new
ImageMosaic Data Sourcelike we already done before and provide the following parametersProvide the following inputs on the
ImageMosaicformName:
boulder_bg_optimizedTitle:
boulder_bg_optimizedURL*:
file:/opt/data/sample_data/user_data/optimized
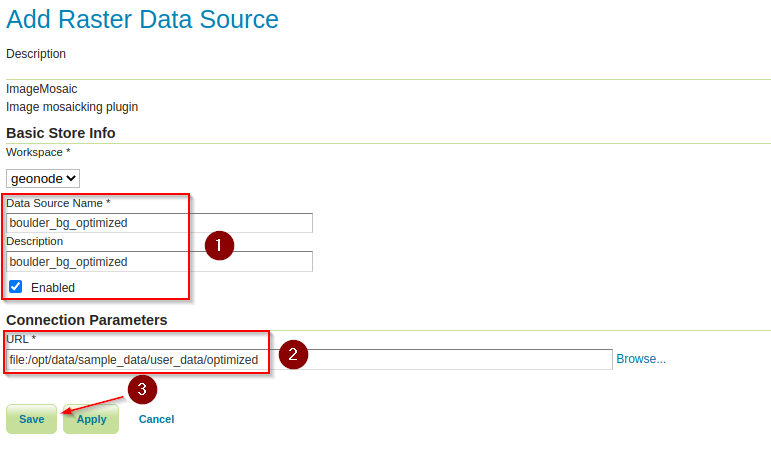
On the next windows, click on
Publish, change the name and title toboulder_bg_optimizedandSavethe layer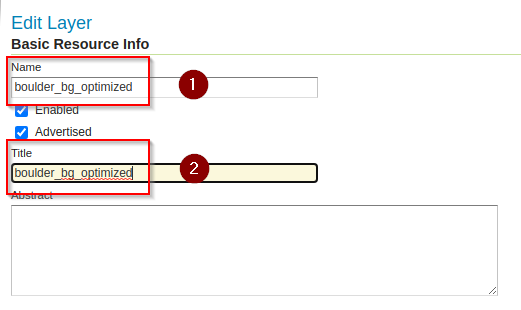
Open the GeoServer
Layer Previewand zoom/pan around, notice how faster is now the mosaic…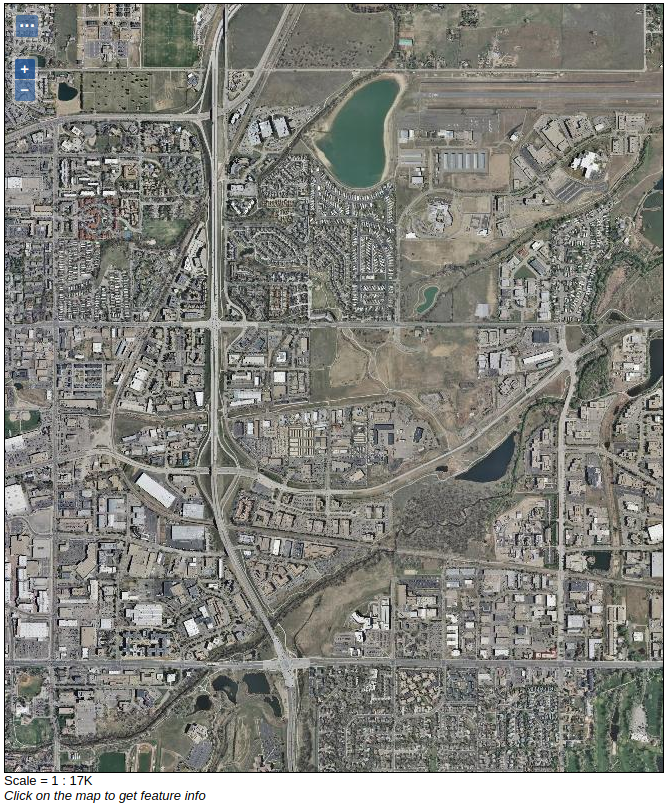
The black tiles are still present.
Let’s customize the mosaic options in order to improve the quality and remove the black tiles.
Customize the
ImageMosaicproperties. Set theOutputTransparentColorto the value000000(Which is theBlackcolor). Click onSavewhen done.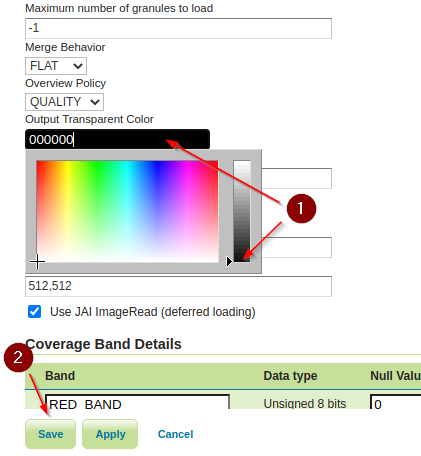
Open the GeoServer
Layer Preview, clear the browser image cache and zoom/pan around, notice the black tiles now gone
Image Mosaic Options¶
There are plenty of options that can be tweaked in order to further optimize an ImageMosaic.
Accurate resolution computation: If
true, computes the resolution of the granules in 9 points, the corners of the requested area and the middle points and take the better one. This will provide better results for cases where there is a lot more deformation on a subregion (top/bottom/sides) of the requested bbox with respect to others. Otherwise, compute the resolution using a basic affine scale transform.AllowMultithreading: If
true, enables tiles multithreading loading. This allows to perform parallelized loading of the granules that compose the mosaic.BackgroundValues: Sets the value of the mosaic
background. Depending on the nature of the mosaic it is wise to set a value for theno dataarea (usually-9999). This value is repeated on all the mosaic bands.Bands: a comma separated list of band indexes that allows to expose only a particular subset of bands out of a multiband source. Normally not configured by hand, but driven by
SLDstyling instead.ExcessGranuleRemoval: An option that should be enabled when using scattered and deeply overlapping images. By default the image mosaic will try to mosaic toghether all images in the requested area, even if some are behind and won’t show up in the final image. With excess granule removal the system will use the image footprint to determine which granules actually contribute pixels to the output, and will end up performing the image processing only on those actually contributing. Best used along with footprints and sorting (to control which images actually stay on top). Possible values are
NONEorROI(Region Of Interest).Filter: Filters granules based on attributes from the input coverage.
Footprint Behavior: Sets the behavior of the regions of a granule that are outside of the granule footprint. Can be
None(Ignore the footprint),Cut(Remove regions outside the footprint from the image. Does not add an alpha channel), orTransparent(Make regions outside the footprint completely transparent. Will add an alpha channel if one is not already present). Defaults toNone.InputTransparentColor: Sets the transparent color for the granules prior to mosaicking them in order to control the superimposition process between them. When GeoServer composes the granules to satisfy the user request, some of them can overlap some others, therefore, setting this parameter with the opportune color avoids the overlap of no data areas between granules.
MaxAllowedTiles: Sets the maximum number of the tiles that can be load simultaneously for a request. In case of a large mosaic this parameter should be opportunely set to not saturating the server with too many granules loaded at the same time.
MergeBehavior: Merging behaviour for the various granules of the mosaic that GeoServer will produce. This parameter controls whether we want to merge in a single mosaic or stack all the bands into the final mosaic.
OVERVIEW_POLICY: Policy used to select the best matching overview for a given target output resolution. Possible values are
QUALITY(pick an overview with a higher resolution and downsample),NEAREST(pick the one with the closest resolution),SPEED(pick the closest one with lower resolution) andIGNORE(do not use overviews).OutputTransparentColor: Sets the transparent color for the created mosaic.
SORTING: Allows to specify the time order of the obtained granules set. Valid values are
DESC(descending) orASC(ascending). Note that it works just by usingDBMSas indexes.SUGGESTED_TILE_SIZE: Controls the tile size of the input granules as well as the tile size of the output mosaic. It consists of two positive integers separated by a comma, like
512,512.USE_JAI_IMAGEREAD: If
true, GeoServer will make use ofJAI ImageReadoperation and its deferred loading mechanism to load granules; iffalse, GeoServer will perform directImageIOread calls which will result in immediate loading.
Introduction To Processing With GDAL Utilities¶
It’s a common practice to do a preliminary analysis on the available data and, if needed, optimize it, since configuring big layers without proper pre-processing, may result in low performance when accessing them.
The previous examples show the difference between a non-optimized and an optimized mosaic, i.e. mosaics with pre-processed GeoTIFF granules or nor.
In this section, instructions about how to do data optimization will be provided by introducing some of the GDAL Utilities.
gdalinfo¶
This utility allows to get several info from the GDAL library, for instance, specific Driver capabilities and input Layers/Files properties.
gdalinfo - Getting Drivers Capabilities¶
Being GeoTIFF a widely adopted geospatial format, it’s useful to get information about the GDAL GeoTIFF’s Driver capabilities using the command
gdalinfo --format GTIFF
Format Details:
Short Name: GTiff
Long Name: GeoTIFF
Supports: Raster
Extensions: tif tiff
Mime Type: image/tiff
Help Topic: drivers/raster/gtiff.html
Supports: Sublayers
Supports: Open() - Open existing layer.
Supports: Create() - Create writable layer.
Supports: CreateCopy() - Create layer by copying another.
Supports: Virtual IO - eg. /vsimem/
Creation Datatypes: Byte UInt16 Int16 UInt32 Int32 Float32 Float64 CInt16 CInt32 CFloat32 CFloat64
<CreationOptionList>
<Option name="COMPRESS" type="string-select">
<Value>NONE</Value>
<Value>LZW</Value>
<Value>PACKBITS</Value>
<Value>JPEG</Value>
<Value>CCITTRLE</Value>
<Value>CCITTFAX3</Value>
<Value>CCITTFAX4</Value>
<Value>DEFLATE</Value>
<Value>LZMA</Value>
<Value>ZSTD</Value>
<Value>WEBP</Value>
</Option>
<Option name="PREDICTOR" type="int" description="Predictor Type (1=default, 2=horizontal differencing, 3=floating point prediction)" />
<Option name="DISCARD_LSB" type="string" description="Number of least-significant bits to set to clear as a single value or comma-separated list of values for per-band values" />
<Option name="JPEG_QUALITY" type="int" description="JPEG quality 1-100" default="75" />
<Option name="JPEGTABLESMODE" type="int" description="Content of JPEGTABLES tag. 0=no JPEGTABLES tag, 1=Quantization tables only, 2=Huffman tables only, 3=Both" default="1" />
<Option name="ZLEVEL" type="int" description="DEFLATE compression level 1-9" default="6" />
<Option name="LZMA_PRESET" type="int" description="LZMA compression level 0(fast)-9(slow)" default="6" />
<Option name="ZSTD_LEVEL" type="int" description="ZSTD compression level 1(fast)-22(slow)" default="9" />
<Option name="WEBP_LEVEL" type="int" description="WEBP quality level. Low values result in higher compression ratios" default="75" />
<Option name="NUM_THREADS" type="string" description="Number of worker threads for compression. Can be set to ALL_CPUS" default="1" />
<Option name="NBITS" type="int" description="BITS for sub-byte files (1-7), sub-uint16_t (9-15), sub-uint32_t (17-31), or float32 (16)" />
<Option name="INTERLEAVE" type="string-select" default="PIXEL">
<Value>BAND</Value>
<Value>PIXEL</Value>
</Option>
<Option name="TILED" type="boolean" description="Switch to tiled format" />
<Option name="TFW" type="boolean" description="Write out world file" />
<Option name="RPB" type="boolean" description="Write out .RPB (RPC) file" />
<Option name="RPCTXT" type="boolean" description="Write out _RPC.TXT file" />
<Option name="BLOCKXSIZE" type="int" description="Tile Width" />
<Option name="BLOCKYSIZE" type="int" description="Tile/Strip Height" />
<Option name="PHOTOMETRIC" type="string-select">
<Value>MINISBLACK</Value>
<Value>MINISWHITE</Value>
<Value>PALETTE</Value>
<Value>RGB</Value>
<Value>CMYK</Value>
<Value>YCBCR</Value>
<Value>CIELAB</Value>
<Value>ICCLAB</Value>
<Value>ITULAB</Value>
</Option>
<Option name="SPARSE_OK" type="boolean" description="Should empty blocks be omitted on disk?" default="FALSE" />
<Option name="ALPHA" type="string-select" description="Mark first extrasample as being alpha">
<Value>NON-PREMULTIPLIED</Value>
<Value>PREMULTIPLIED</Value>
<Value>UNSPECIFIED</Value>
<Value aliasOf="NON-PREMULTIPLIED">YES</Value>
<Value aliasOf="UNSPECIFIED">NO</Value>
</Option>
<Option name="PROFILE" type="string-select" default="GDALGeoTIFF">
<Value>GDALGeoTIFF</Value>
<Value>GeoTIFF</Value>
<Value>BASELINE</Value>
</Option>
<Option name="PIXELTYPE" type="string-select">
<Value>DEFAULT</Value>
<Value>SIGNEDBYTE</Value>
</Option>
<Option name="BIGTIFF" type="string-select" description="Force creation of BigTIFF file">
<Value>YES</Value>
<Value>NO</Value>
<Value>IF_NEEDED</Value>
<Value>IF_SAFER</Value>
</Option>
<Option name="ENDIANNESS" type="string-select" default="NATIVE" description="Force endianness of created file. For DEBUG purpose mostly">
<Value>NATIVE</Value>
<Value>INVERTED</Value>
<Value>LITTLE</Value>
<Value>BIG</Value>
</Option>
<Option name="COPY_SRC_OVERVIEWS" type="boolean" default="NO" description="Force copy of overviews of source layer (CreateCopy())" />
<Option name="SOURCE_ICC_PROFILE" type="string" description="ICC profile" />
<Option name="SOURCE_PRIMARIES_RED" type="string" description="x,y,1.0 (xyY) red chromaticity" />
<Option name="SOURCE_PRIMARIES_GREEN" type="string" description="x,y,1.0 (xyY) green chromaticity" />
<Option name="SOURCE_PRIMARIES_BLUE" type="string" description="x,y,1.0 (xyY) blue chromaticity" />
<Option name="SOURCE_WHITEPOINT" type="string" description="x,y,1.0 (xyY) whitepoint" />
<Option name="TIFFTAG_TRANSFERFUNCTION_RED" type="string" description="Transfer function for red" />
<Option name="TIFFTAG_TRANSFERFUNCTION_GREEN" type="string" description="Transfer function for green" />
<Option name="TIFFTAG_TRANSFERFUNCTION_BLUE" type="string" description="Transfer function for blue" />
<Option name="TIFFTAG_TRANSFERRANGE_BLACK" type="string" description="Transfer range for black" />
<Option name="TIFFTAG_TRANSFERRANGE_WHITE" type="string" description="Transfer range for white" />
<Option name="STREAMABLE_OUTPUT" type="boolean" default="NO" description="Enforce a mode compatible with a streamable file" />
<Option name="GEOTIFF_KEYS_FLAVOR" type="string-select" default="STANDARD" description="Which flavor of GeoTIFF keys must be used">
<Value>STANDARD</Value>
<Value>ESRI_PE</Value>
</Option>
<Option name="GEOTIFF_VERSION" type="string-select" default="AUTO" description="Which version of GeoTIFF must be used">
<Value>AUTO</Value>
<Value>1.0</Value>
<Value>1.1</Value>
</Option>
</CreationOptionList>
<OpenOptionList>
<Option name="NUM_THREADS" type="string" description="Number of worker threads for compression. Can be set to ALL_CPUS" default="1" />
<Option name="GEOTIFF_KEYS_FLAVOR" type="string-select" default="STANDARD" description="Which flavor of GeoTIFF keys must be used (for writing)">
<Value>STANDARD</Value>
<Value>ESRI_PE</Value>
</Option>
<Option name="GEOREF_SOURCES" type="string" description="Comma separated list made with values INTERNAL/TABFILE/WORLDFILE/PAM/NONE that describe the priority order for georeferencing" default="PAM,INTERNAL,TABFILE,WORLDFILE" />
<Option name="SPARSE_OK" type="boolean" description="Should empty blocks be omitted on disk?" default="FALSE" />
</OpenOptionList>
Other metadata items:
LIBGEOTIFF=1700
LIBTIFF=LIBTIFF, Version 4.1.0
Copyright (c) 1988-1996 Sam Leffler
Copyright (c) 1991-1996 Silicon Graphics, Inc.
From the list of create options above, it’s possible to determine the main GeoTIFF Driver’s writing capabilities:
COMPRESS: customize the compression to be used when writing output dataJPEG_QUALITY: specify a quality factor to be used by theJPEGcompressionTILED: When set toYESit allows to tiled output dataBLOCKXSIZE, BLOCKYZISE: Specify the Tile dimension width and Tile dimension heightPHOTOMETRIC: Specify the photometric interpretation of the dataPROFILE: Specify theGeoTIFFprofile to be used (some profiles only support a minimal set ofTIFF Tagswhile some others provide a wider range ofTags)BIGTIFF: Specify when to write data asBigTIFF(ATIFFformat which allows to break the4GB Offsetboundary)
gdalinfo - Getting Layer/File Properties¶
The following instructions allow you to get information about the sample layer previously configured in GeoServer
cd /opt/data/sample_data/user_data/aerial
gdalinfo 13tde815295_200803_0x6000m_cl.tif
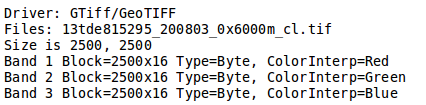
Part of the gdalinfo output on a sample layer.
Block: It represents the internal tiling. Notice that the sample layer has tiles made of 16 rows having width equals to the full image width.
Overviews: It provides information about the underlying overviews. Notice that the sample layer doesn’t have overviews since the Overviews property is totally missing from the gdalinfo output.
gdal_translate¶
This utility allows to convert a layer to a different format by allowing a wide set of parameters to customize the conversion.
Running the command
gdal_translate
allows to get the list of supported parameters as well as the supported output formats
Usage: gdal_translate [--help-general]
[-ot {Byte/Int16/UInt16/UInt32/Int32/Float32/Float64/
CInt16/CInt32/CFloat32/CFloat64}] [-strict]
[-of format] [-b band] [-mask band] [-expand {gray|rgb|rgba}]
[-outsize xsize[%] ysize[%]]
[- unscale] [-scale [src_min src_max [dst_min dst_max]]]
[-srcwin xoff yoff xsize ysize] [-projwin ulx uly lrx lry]
[-a_srs srs_def] [-a_ullr ulx uly lrx lry] [-a_nodata value]
[-gcp pixel line easting northing [elevation]]*
[-mo "META-TAG=VALUE"]* [-q] [-sds]
[-co "NAME=VALUE"]* [-stats]
src_layer dst_layer
The meaning of the main parameters is summarized below
-ot: allows to specify the output datatype (Make sure that the specified datatype is contained in the Creation Datatypes list of the Writing driver)-of: specify the desired output format (GTIFF is the default value)-b: allows to specify an input band to be written in the output file. (Use multiple -b option to specify more bands)-mask: allows to specify an input band to be write an output layer mask band.-expand: allows to expose a layer with 1 band with a color table as a layer with 3 (rgb) or 4 (rgba) bands. The (gray) value allows to expand a layer with a color table containing only gray levels to a gray indexed layer.-outsize: allows to set the size of the output file in terms of pixels and lines unless the % sign is attached in which case it’s as a fraction of the input image size.-unscale: allows to apply the scale/offset metadata for the bands to convert from scaled values to unscaled ones.-scale: allows to rescale the input pixels values from the range src_min to src_max to the range dst_min to dst_max. (If omitted the output range is 0 to 255. If omitted the input range is automatically computed from the source data).-srcwin: allows to select a subwindow from the source image in terms of xoffset, yoffset, width and height-projwin: allows to select a subwindow from the source image by specifying the corners given in georeferenced coordinates.-a_srs: allows to override the projection for the output file. The srs_def may be any of the usual GDAL/OGR forms, complete WKT, PROJ.4, EPSG:n or a file containing the WKT.-a_ullr: allows to assign/override the georeferenced bounds of the output file.-a_nodata: allows to assign a specified nodata value to output bands.-co: allows to set a creation option in the form “NAME=VALUE” to the output format driver. (Multiple -co options may be listed.)-stats: allows to get statistics (min, max, mean, stdDev) for each bandsrc_layer: is the source layer name. It can be either file name, URL of data source or sublayer name for multi*-layer files.dst_layer: is the destination file name.
gdal_translate - Tiling the sample layer¶
The following steps provide instructions to tile the sample layer previously configured in GeoServer, by using the GeoTiff driver.
Move to the parent folder
/opt/data/sample_data/user_datacd /opt/data/sample_data/user_dataConvert the input sample data to an output file having tiling set to
512x512(the compression parameters are explained in).gdal_translate -co "TILED=YES" -co "BLOCKXSIZE=512" -co "BLOCKYSIZE=512" -co "COMPRESS=JPEG" -co "PHOTOMETRIC=YCBCR" -co "QUALITY=85" aerial/13tde815295_200803_0x6000m_cl.tif retiled/13tde815295_200803_0x6000m_cl.tif
Check that the output layer has successfully been tiled, by running the command
gdalinfo retiled/13tde815295_200803_0x6000m_cl.tif
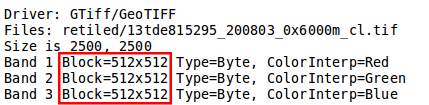
Part of the gdalinfo output on the tiled layer. Notice the Block value now is 512x512.
gdaladdo¶
This utility allows to add overviews to a layer. The following steps provide instructions to add overviews to the tiled sample layer.
Running the command
gdaladdo
allows to get the list of supported parameters
Usage: gdaladdo [-r {nearest,average,gauss,average_mp,average_magphase,mode}]
[-ro] [--help-general] filename levels
The meaning of the main parameters is summarized below
-r: allows to specify the resampling algorithm (Nearest is the default value)-ro: allows to open the layer in read-only mode, in order to generate external overview (for GeoTIFF especially)filename: represents the file to build overviews for.levels: allows to specify a list of overview levels to build.
gdaladdo - Adding overviews to the sample layer¶
Move to the
retiledfoldercd retiledRun the
gdaladdocommand as followsgdaladdo -r average --config COMPRESS_OVERVIEW JPEG --config PHOTOMETRIC_OVERVIEW YCBCR --config JPEG_QUALITY_OVERVIEW 85 13tde815295_200803_0x6000m_cl.tif 2 4 8 16 32
Check that the overviews have been added to the layer, by running the command
gdalinfo 13tde815295_200803_0x6000m_cl.tif
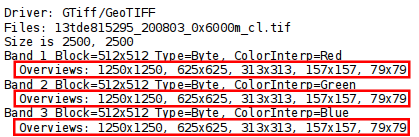
Part of the gdalinfo output on the tiled layer with overviews. Notice the Overviews properties.
Process in Bulk¶
Instead of manually repeating these 2 steps (retile + add overviews) for each file, we can invoke a few commands to get it automated.
cd /opt/data/sample_data/user_data/aerial
for i in `find *.tif`; do gdal_translate -CO "TILED=YES" -CO "BLOCKXSIZE=512" -CO "BLOCKYSIZE=512" -co "COMPRESS=JPEG" -co "PHOTOMETRIC=YCBCR" -co "QUALITY=85" $i ../optimized/$i; gdaladdo -r average --config COMPRESS_OVERVIEW JPEG --config PHOTOMETRIC_OVERVIEW YCBCR --config JPEG_QUALITY_OVERVIEW 85 ../optimized/$i 2 4 8 16 32; done
You should see a list of run like this
...
Input file size is 2500, 2500
0...10...20...30...40...50...60...70...80...90...100 - done.
0...10...20...30...40...50...60...70...80...90...100 - done.
Input file size is 2500, 2500
0...10...20...30...40...50...60...70...80...90...100 - done.
0...10...20...30...40...50...60...70...80...90...100 - done.
Input file size is 2500, 2500
0...10...20...30...40...50...60...70...80...90...100 - done.
0...10...20...30...40...50...60...70...80...90...100 - done.
...
At this point optimized layers have been prepared and they are ready to be served by GeoServer as an ImageMosaic.
gdalwarp¶
This utility allows to warp and reproject a layer. The following steps provide instructions to reproject the aerial layer (which has EPSG:26913 coordinate reference system) to WGS84 (EPSG:4326).
Running the command
gdalwarp
allows to get the list of supported parameters
Usage: gdalwarp [--help-general] [--formats]
[-s_srs srs_def] [-t_srs srs_def] [-to "NAME=VALUE"]
[-order n | -tps | -rpc | -geoloc] [-et err_threshold]
[-refine_gcps tolerance [minimum_gcps]]
[-te xmin ymin xmax ymax] [-tr xres yres] [-tap] [-ts width height]
[-wo "NAME=VALUE"] [-ot Byte/Int16/...] [-wt Byte/Int16]
[-srcnodata "value [value...]"] [-dstnodata "value [value...]"] -dstalpha
[-r resampling_method] [-wm memory_in_mb] [-multi] [-q]
[-cutline datasource] [-cl layer] [-cwhere expression]
[-csql statement] [-cblend dist_in_pixels] [-crop_to_cutline]
[-of format] [-co "NAME=VALUE"]* [-overwrite]
srcfile* dstfile
The meaning of the main parameters is summarized below
-s_srs: allows to specify the source coordinate reference system-t_srs: allows to specify the target coordinate reference system-te: allows to set georeferenced extents (expressed in target CRS) of the output-tr: allows to specify the output resolution (expressed in target georeferenced units)-ts: allows to specify the output size in pixel and lines.-r: allows to specify the resampling method (one ofnear,bilinear,cubic,cubicsplineandlanczos)-srcnodata: allows to specify band values to be excluded from interpolation.-dstnodata: allows to specify nodata values on output file.-wm: allows to specify the amount of memory (expressed in megabytes) used by the warping API for caching.
gdalwarp - Reprojecting sample layer to WGS84¶
Move to the
/opt/data/sample_data/user_data/retiledfoldercd /opt/data/sample_data/user_data/retiledRun the
gdalwarpcommandgdalwarp -t_srs "EPSG:4326" -co "TILED=YES" 13tde815295_200803_0x6000m_cl.tif 13tde815295_200803_0x6000m_cl_warped.tif
Check that reprojection has been successfull, by running the command
gdalinfo 13tde815295_200803_0x6000m_cl_warped.tif
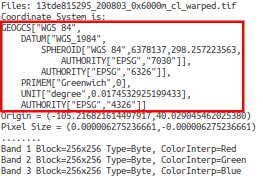
Part of the gdalinfo output on the warped layer. Notice the updated Coordinate System property.
Further Reading about GDAL¶
https://geoserver.geo-solutions.it/educational/en/raster_data/advanced_gdal/index.html
Publish the Optimized Mosaic on GeoNode¶
Activate the
geonodevirtual env and move to/opt/geonodeRun the
updatelayersmanagement command as follows./manage_local.sh updatelayers --skip-geonode-registered -u test_user1 -w geonode -f boulder_bg_optimized
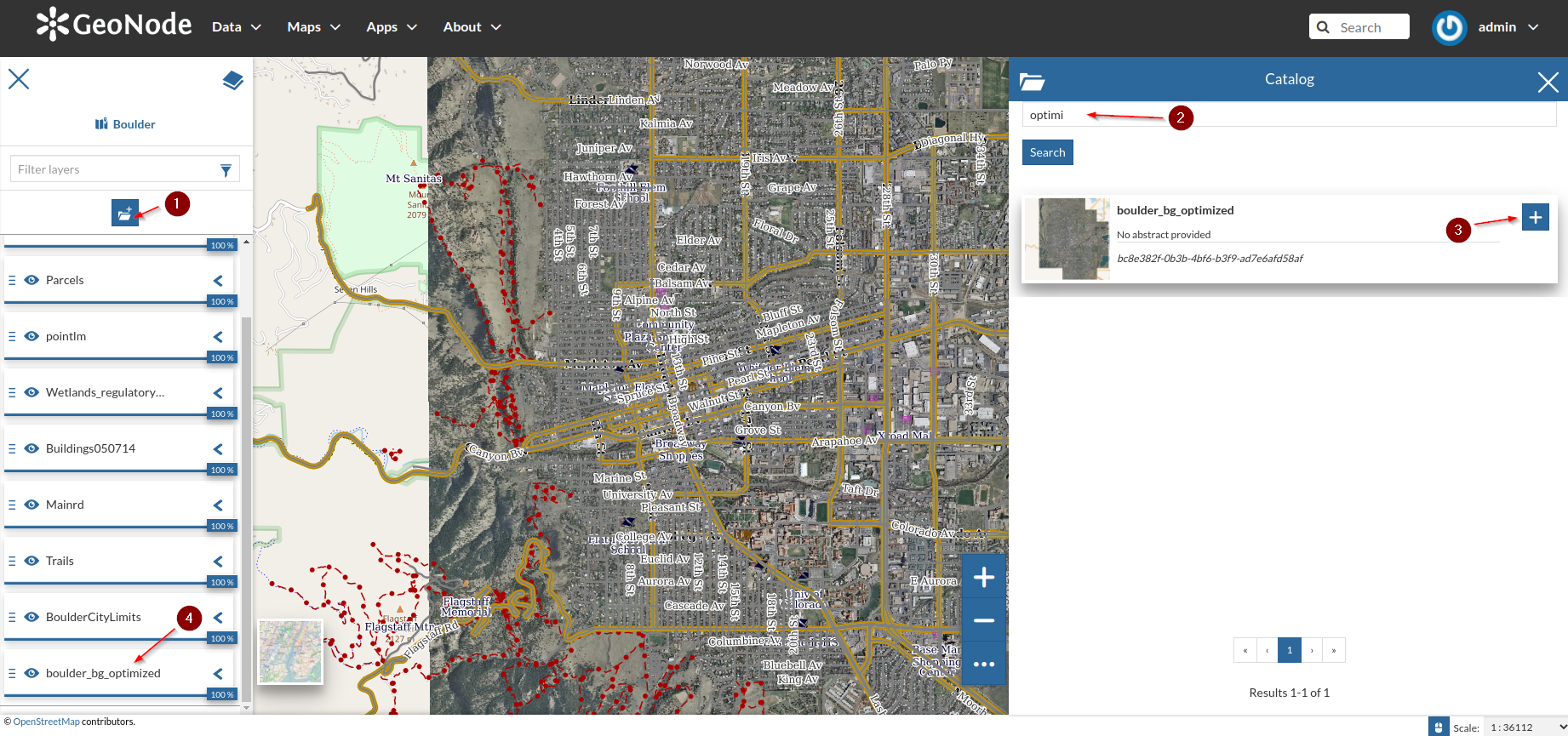
Verify the new layer has been succesfully created on GeoNode
Add the new layer to the
Bouldermap, and drag it to the bottom