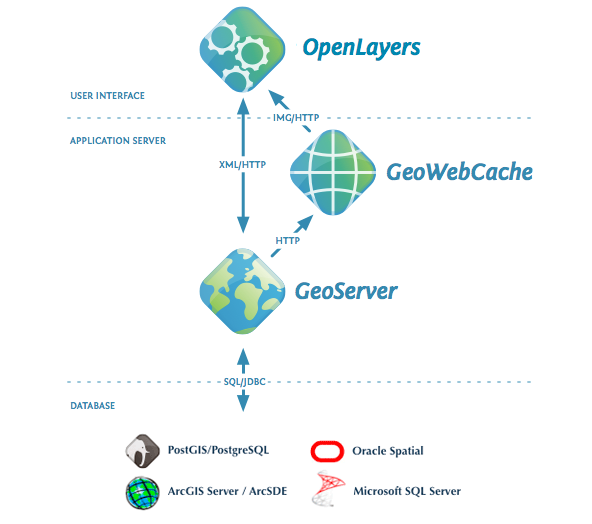
GeoNode Basics¶

is a platform for the management and publication of geospatial data. It brings together mature open-source software projects under an easy to use interface.
Geospatial data storage¶
GeoNode allows users to upload vector data (currently shapefiles, json, csv, kml and kmz) and raster data in their original projections using a web form.
Vector data is converted into geospatial tables on a DB, satellite imagery and other kinds of raster data are retained as GeoTIFFs.
Special importance is given to standard metadata formats like ISO 19139:2007 / ISO 19115 metadata standards.
As soon as the upload is finished, the user can fill the resource metadata in order to make it suddenly available through the CSW (OGC Catalogue Service) endpoints and APIs.
Users may also upload a metadata XML document (ISO, FGDC, and Dublin Core format) to fill key GeoNode metadata elements automatically.
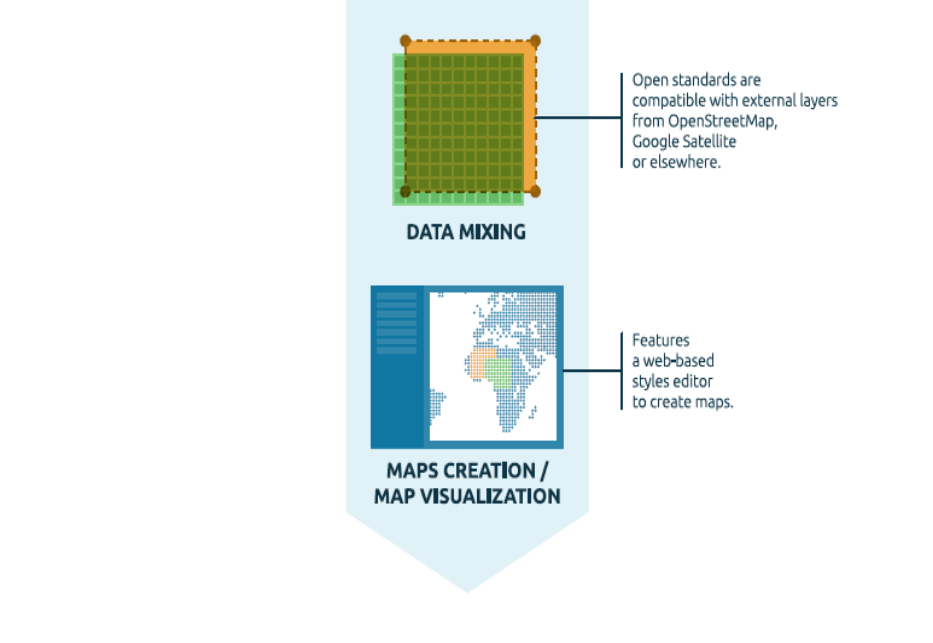
Similarly, GeoNode provides a web based styler that lets the users to change the data portrayals and preview the changes at real time.
Data mixing, maps creation¶
Once the data has been uploaded, GeoNode lets the user search for it geographically or via keywords in order to create fancy maps.
All the layers are automatically re-projected to web Mercator for maps display, making it possible to use different popular base layers, like Open Street Map, Google Satellite or Bing layers.
Once the maps are saved, it is possible to embed them in any web page or get a PDF version for printing.
GeoNode as a building block¶
A handful of other Open Source projects extend GeoNode’s functionality by tapping into the re-usability of Django applications.
GeoNode can be integrated on other Django applications as a dependency or as a building block of a wider architecture.
Thanks to the GeoNode APIs, it is possible to use the component as a pure middleware and/or backend and storage for your geospatial layers.
Thanks to the compatibility with standard security protocols, it can be used as a security framework and users’ credentials storage.